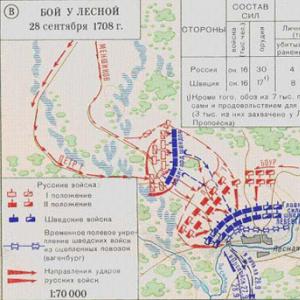
Is the mottled oak mushroom edible or not? Large does not mean edible: a detailed description of the oak tree. Where do oak mushrooms grow?
Dubovik is a mushroom that speaks for itself, growing under oak trees in deciduous forests. It is very similar to boletus, but also has some differences. The boletus family includes not only edible species dubovikov, but also a well-known satanic mushroom that poses a serious danger to the human body.
Other names for the mushroom
The mushroom stem is covered with a kind of dark mesh, by which one can distinguish the common oak. The oak mushroom has a brown color with different shades, which is why it is also called:
- olive-brown oakwood;
- underdubnik;
- subdukovik;
- dirty brown ache.
Description and features of oak wood. What does a mushroom look like?
The mushroom itself is tasty and has a pleasant aroma, but it is important not to confuse it with others that are less tasty and less healthy mushrooms. To do this, you should familiarize yourself with its appearance.
hat has a large diameter that can reach 20 centimeters. The cap is massive, fleshy, hemisphere shaped. It is practically not attached to the leg, we can say that it is put on it. Over time, it opens up and becomes like a pillow. The top is velvety, having different colors: yellow-brown, gray-brown, dark orange. The cap is painted unevenly. The pulp is yellow, and at the fracture site it acquires a blue-green color.
Leg quite thick, massive, club-shaped, the height of which is up to 12 centimeters. Under the cap the leg is yellow in color, and the lower it goes, the darker the color and at the very root it is dark orange. A distinctive feature of the mushroom is the mesh that covers the stem; the flesh is red.
Pulp yellow in color, when cut with strong pressure or when exposed to air, it turns blue. The taste and aroma are pleasant, but not pronounced.
If you eat dubovik mushroom together with alcoholic drinks, severe poisoning is possible.

When and where can you find a mushroom?
The mushroom grows on limestone soil, where the sun warms the ground well, they can often be found near:
- birch;
- oak;
- fir trees
The oak harvest season begins from May to June, then they disappear and come out of the ground again in August and September.
Varieties
The common oak also has varieties that are identical in composition to the original, but have a different appearance and size.
Speckled oakweed
Speckled oakberry is an edible mushroom with a pleasant taste and aroma.
hat velvety, can be brown, dark blue, chestnut or brown, which darkens with the slightest pressure on the flesh. The shape is pillow-shaped or hemispherical.
Leg reaches 16 centimeters in height and has a red-yellow hue, covered with dots or a kind of mesh.
Pulp bright yellow or orange; at the site of a break or cut, it acquires a bluish tint over time. There is no strong taste or aroma.

Doubles. Satanic mushroom (poisonous), at the site of the break the flesh turns red and only after that acquires a bluish tint. The yellow boletus differs in that the mushroom has a completely yellow stem and can only be found in Western Europe. Kele's oak mushroom is a very rare species of mushroom that grows only on calcareous soil.
When and where can we meet? The mushroom grows from May to October:
- in Siberia;
- in the Caucasus;
- Far East;
- European part of Russia.
Sometimes found in Leningrad. In coniferous and deciduous forests, on swampy and acidic soils near spruce, fir and oak.
An edible mushroom belonging to the boletus genus, the taste and aroma are not pronounced.
hat convex, 20 centimeters in diameter, rarely flat. The color is brown with an olive tint, sometimes a yellow-brown tint. The edges of the hat are reddish, and the bottom is tubular and burgundy in color.
Leg 12 centimeters high, the color is the same as the hat.

Pulp fleshy, turns green at the break point. It has a pleasant, not pronounced taste and aroma.
When and where can we meet? Most often, olive-brown butterfly is found in deciduous and mixed forests in the lowlands. It mainly grows near or under oak trees, hence the name. It grows from July to September.
What can the common oak tree be confused with?
The common oak mushroom is a bit similar to other mushrooms, both poisonous and edible. Before putting a mushroom in a basket, you need to inspect it and make sure that this mushroom will not harm your health.
Dubovik can be confused with the following mushrooms:
- speckled oakberry (edible mushroom);
- pink-golden oakberry (edible after heat treatment, but poisonous when raw);
- satanic mushroom (poisonous even after heat treatment).
This type of mushroom is not found often, but still, if a person does not understand mushrooms, then it is better not to collect oak trees. Of course there will be no lethal outcome, but serious poisoning can occur.

Processing and Application
In order to be able to eat the oak mushroom, it should be soaked for half a day, during which time it is necessary to change the water to clean water every 1-2 hours. Then they are boiled and only after that it can be prepared according to the recipe you like. Although there are few toxins in this mushroom, they are still destroyed during cooking. If mushrooms are not properly processed, this can lead to problems. gastrointestinal tract.
You can pickle duboviks, and if you throw a little into the jar citric acid, the mushroom will retain its color even after long-term storage.
You can also first boil the dubovik, then fry it, seasoning it with your favorite sauce. In addition, mushroom-based soups, sauces, and dressings are made in addition to side dishes. Even with heat treatment, oakwood does not lose its value, smells good and has good taste.
Value in medicine
IN folk medicine oak trees became famous as medicine against malignant tumors. For a long time, lotions and balms have been made from these mushrooms, the application of which reduces fatigue, eliminates depression, calms the nerves and eliminates fatigue.
Benefits and beneficial values of oakberry
All edible mushrooms contain many useful acids, vitamins and microelements. The common oak mushroom does not lag behind the others and also has many useful substances. The main components are zinc, magnesium and iron, which have reducing properties and others useful material.

Zinc– useful for the proper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. This microelement is able to accumulate in the pancreas, takes part in digestion, and helps to properly absorb nutrients.
Copper– restores cells, improves metabolism, forms hormones and improves blood circulation.
Iron– normalizes the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. Systematic intake of oakberry, even in minimal quantities, replenishes the body's need for important components.
Amino acids– can improve mental and visual memory, add energy, vigor and strength, increase mental activity, and also prevent the development of atherosclerosis.
Beta glucans– contained in common oak trees in large quantities have a positive effect on the human immune system.
Contraindications and harm
In general, oak mushrooms cannot harm the body; it is important to collect them correctly, without confusing them with a poisonous satanic mushroom, because they are similar in appearance. The main difference is the unpleasant pungent odor and poisonous mushroom the cap is greenish in color.
Mushrooms are a specific food that contains a large number of chitin. They undoubtedly benefit the body, but it is important to understand that children under 12 years of age have not yet developed enzymes that will allow this product to be well absorbed. Therefore, in childhood there is no need to give dishes with the presence of mushrooms, in order to avoid unpleasant consequences. Also, mushrooms should not be consumed by people who suffer from allergic reaction.

Mushroom cultivation
Many mushroom lovers or simply summer residents want to have edible and delicious mushrooms, but few people know where to start and how this process even happens.
There are two ways to grow oak trees:
- extensive;
- intensive.
Extensive
Thanks to the first method of growing mushrooms, in which all conditions are as close to natural as possible, there is a greater chance of getting a large harvest. This method does not require special equipment or any skills. The only bad thing is that everything depends on the weather conditions and climate; if the weather is bad, then the mushrooms will bear fruit worse and slower.
It is necessary to grow oak mushrooms near deciduous trees, preferably near an oak tree. The plantation where oak trees will grow must be protected from the sun, that is, direct rays should not fall. Around the tree, 20 centimeters thick soil is removed, approximately one square meter. This area should be watered well, then sprinkled with soil prepared as follows:
- mix peat;
- leaves from a tree;
- sawdust;
- horse dung.
Mix everything with soil and lay it around the trunk. On top of this, sprinkle the mycelium with dry soil and cover it with the native soil removed earlier and “drip” it. In the hot summer months, the soil should be watered periodically, and in winter it should be insulated with moss, leaves that have fallen from the tree and straw. You can start such planting in spring or summer; if everything was done correctly, then after 6 months you can harvest the first harvest.

Speckled oakweed or granulopod also has names such as boletus, granulopod, and red-legged boletus. The mushroom can be found from August to September in deciduous and spruce forests. In the middle zone and the Moscow region, mushroom baskets are a rather rare guest. In the south of Russia, the first specimens are found at the end of May.
The beautiful mushroom has a hemispherical cap that is chestnut brown or dark Brown with a light edge. The surface is dry, matte. Velvety at first, becoming smooth with age. The tubular layer is yellow-olive to red-orange in color, darkening blue when pressed. The stem is tuberous-barrel-shaped, up to 10 cm long and 3-4 cm in diameter. The stem is yellow-red in color with small reddish speckled scales located randomly. The flesh is dense, fleshy, yellow in color, and in the leg it is reddish, quickly turning blue when cut.
A good edible mushroom. Requires preliminary boiling for fifteen minutes, draining the liquid.
Photos of oak oaks


Description of the Speckled or Granulopod Oak in pictures

The oak mushroom, often called the oak mushroom, as the name suggests, grows in deciduous forests, mainly in oak groves. You can find out what the dubovik mushroom looks like by remembering everyone’s favorite boletus mushroom. In many ways, these gifts of the forest are similar in appearance, but of course, there are a number of differences.
On this page you can see a photo and description of the oak mushroom, learn about the halo of its distribution and application. You will also receive information about the most common types of oak: common and speckled.
Cap of the common oak tree (Boletus luridus) (diameter 6-22 cm): from brown to light olive; in older mushrooms it can darken to black-brown. Sometimes they remain when pressed dark spots. Usually has the shape of a hemisphere, occasionally it can be almost prostrate. Velvety to the touch, sticky and slippery in wet weather or after rain.


Pay attention to the leg of the common oak tree: its height is 5-17 cm, most often it is red, dark orange or brown, there may be small greenish spots at the very base. It has the shape of a club, a characteristic tuberous thickening and a mesh pattern along its entire length. Tubular layer: with round and very small red pores that turn blue when gently pressed.
Pulp: yellow, turns blue when cut and when exposed to air. Does not have a pronounced taste or smell.
Doubles: none.
When it grows: from the end of May to the beginning of September in the Caucasus, Siberia and Far East. Although it is a heat-loving mushroom, it can also be found in the Leningrad region.
Use in folk medicine: is not used, but scientists have learned to extract the antibiotic boletol from the common oak tree.
Important! Consuming common oakberry along with alcohol can lead to gastrointestinal problems.


Where can I find: on limestone soils next to birch and oak trees in well-warmed and sunny areas of the forest.
Eating: in dried or pickled form, subject to prior soaking and boiling, and the water must be drained several times. Although the concentration of toxic substances in ordinary oak wood is very small, and they are destroyed during cooking, a short temperature treatment can still lead to severe eating disorder. If you add a little citric acid to the jar during pickling, the mushroom will retain the light color of the pulp and will not change it to lilac or purple.
Other names: dubovik olive-brown, podubovik, boletus dirty-brown.
Edible mushroom speckled oak mushroom and its photo
Cap of the edible speckled oak (Boletus erythropus) (diameter 7-22 cm): dark brown, chestnut, black-brown, noticeably darkens even with gentle pressure. It has a hemispheric or cushion shape. Velvety to the touch.
Leg (height 7-16 cm): usually red and yellow, often with dots or a reticulate pattern. Thick, cylindrical or barrel-shaped, tapering from bottom to top.
Tubular layer: with rounded tubes of yellow or orange color. It darkens noticeably when pressed.


The pulp of the speckled oak tree deserves special attention: the photo shows that it is bright yellow or orange, changing color when cut and when interacting with air to bluish or blue. It has no pronounced taste or aroma.
Doubles: poisonous satanic mushroom(Boletus satanas), the flesh of which first turns red when cut, and only then turns blue. Yellow boletus (Boletus junquilleus), which grows only in Western Europe and has a yellow stem. The very rare Kele oak (Boletus queletii), like the olive brown oak (Boletus luridus), grows exclusively on calcareous soils.
Dubovik (Boletus luridus) has many names in Russian: boletus, poddubovik, dubovik bruise, deaf boletus, boletus dirty-brown. This is a representative of the same boletus genus as the famous White mushroom(Boletus edulis), which at one time gave the name to mushrooms as such (initially in Russian the word “mushrooms” meant only white mushrooms, and later only edible mushrooms). Alas, not all of them are edible. The poisonous satanic mushroom (Boletus satanas) also belongs to the same boletus mushrooms.
Photo of oak mushroom
Oak mushroom: description and ecology
Poddubovik is a large mushroom. The size of its cap reaches 20 cm, the length of the leg is 15 cm. The cap is hemispherical or even convex shape. Its color is very variable: from the normal light olive-brown shade it often shifts to yellow, orange-yellow, or even red. The hat is sensitive to damage: you just need to put a little pressure on the oak, and the damaged area will soon turn blue, and then become black-brown, reminiscent of a bruise on a person’s skin after a bruise. It is from this property that the poddubnik received one of its names “bruise”. But this feature makes the color of its cap even less predictable: in some cases it may even turn out to be black-brown with red-yellow edges.
The leg of the undercloth has a barrel-shaped shape, later turning into cylindrical or club-shaped. The color is yellowish with a red “mesh”, at the base it turns into a wine-red shade or even black-brown. There may be reddish spots along the entire length of the leg, and greenish spots at the base.
The flesh of the mushroom is dense, without a distinct odor, and the cap is yellowish. The lower part of the leg is the same wine red as the leg itself in this place. When cut, it turns blue-green and then brown.
Podpodubnik grows in lowland deciduous and mixed forests. Often, as the name suggests, under oak trees, with which it enters into symbiosis (forms mycorrhizae). The collection season is July-September with a peak in August, but depending on the weather, oakwood can sometimes be found from May to November.
Security measures
Poddubnik belongs to the class of conditionally edible mushrooms. This means that it contains a certain amount of toxic substances, but they are destroyed or removed during cooking. It is enough to boil the dubovik for 15 minutes, drain the boiled water, and the danger is eliminated. Unless, of course, it really is a dud.
The fact is that few edible mushrooms “know how” to look as different as the mushroom. Its description shows that the color of its cap can be almost any, and, moreover, in its general appearance, the boletus mushroom resembles other mushrooms of the boletus genus, standing out only in size. Of course, if you confuse the olive-brown oakweed with the speckled oakweed, then nothing bad will happen. However, the poisonous satanic mushroom is a completely different matter.
This inedible twin of the oak tree is very similar in appearance to its edible relative. The color of its cap, although usually lighter, with a grayish tint, often falls within the range acceptable for a cape. In addition, the satanic mushroom has almost the same size and has generally similar properties: its flesh, although less “sensitive,” also darkens when cut. She also gravitates towards yellow color in the cap and to red - in the lower part of the leg.
The poison of the satanic mushroom is not completely destroyed even with heat treatment, and even 1 gram of its substance can cause a severe eating disorder.
It is very important for a mushroom picker to know how to distinguish a satanic mushroom from an oak mushroom. Since the color may well deceive, the main attention should be paid to the properties of the pulp when cut: unlike oak mushroom, the flesh of the satanic mushroom first turns red, and only then turns blue (or even remains reddish). The most important sign: the pulp has a pronounced unpleasant odor, especially in old mushrooms. It is important to take into account both of these features at once: sometimes the smell may be less pronounced, but it is always there.

Common oak family
The ability to recognize the oak mushroom and distinguish it from the satanic mushroom is very important for a mushroom picker, since the oak mushroom is an extremely valuable “prey”. It is so large that only a few pieces are enough to meet the expectations of a “quiet hunt”.
Dubovik (Boletus) - mushrooms belonging to the genus Boletus (Boletus) with the Boletaceae family. To know which oak trees can be eaten, you need to take into account the main differences between edible and.
Dubovik (Boletus) - mushrooms belonging to the genus Boletus from the Boletaceae family
In appearance, oak trees very much resemble the “noble” white gib. As a rule, the size of the cap varies between 6-22 cm, and the color of its surface can vary from light brown to brick shades.
Popularly, such a mushroom is very often called poddubovik, poddubovik or bruise. If the variety received the first two names due to its places of distribution, the latter is explained by the appearance of a very noticeable bluish coloration, both on the cut and when pressing on the pulp. The shape of the cap resembles a hemisphere with a velvety or slimy surface. The leg is relatively high, quite thick and dense. The taste characteristics and mushroom aroma of oak pulp are almost completely absent.
Gallery: oak mushroom (25 photos)
























Varieties of oak trees (video)
Places and season for collecting oak trees
Tubular fruiting bodies They grow especially en masse under oak, forming mycorrhiza with this deciduous tree. Some species are mycorrhizal formers also with deciduous trees such as beech and some spruce forests, preferring acidic and mossy soils. Throughout our country, the very first fruiting bodies appear in the very first days of May.
Edible species of oak trees
The most common types of oak in our country are olive-brown or ordinary, as well as speckled.
Speckled oakweed
Bol.еrythroрus - distinguished by a hemispherical, cushion-shaped or rounded-pillow-shaped, velvety, matte or slimy cap of chestnut brown, dark brown, dark brown or blackish-brown color with a reddish tint.
The pulp is beige-yellow or bright yellow, quickly turning blue or acquiring a greenish-blue color when cut. G There is no fish aroma or pronounced taste. The cylindrical or tuberous-shaped area of the leg does not have a mesh on the surface, but reddish dots or scales may be present. The spores are brown-olive, fusiform, with a smooth surface.

Speckled oakweed
Oak tree olive-brown
Vol.luridus - distinguished by a hemispherical or convex cap, sometimes opening to an almost flat shape, with an olive-beige-brown or greenish-brown, velvety or slimy skin that darkens when touched.
The fruit bodies have yellow and dense pulp, blue when cut, with a mild taste and without a pronounced mushroom aroma. The leg is club-shaped, with a tuberous thickening, yellow-orange or reddish-brown, with a convex and reticulate, loop-type pattern.

Oak tree olive-brown
Poisonous mushroom twins
- oak tree Kele(Bol.queletii) - an inedible variety with a round or convex cap, which is covered with a chestnut-reddish-brown skin. The initial velvety surface disappears with age, and the growing skin is not removed from the fleshy and dense, yellowing pulp. The leg area is similar to a cylinder, with a thickening at the base, without voids, with an almost smooth surface of a yellow-beige-brown color. The tubes on the back of the cap characteristically turn blue as a result of pressure or any other mechanical impact;

Dubovik Kele
- satanic gib(Bol. satanas) - a poisonous variety with a hemispherical or rounded-cushion-shaped, sometimes spread-shaped cap, which is covered with a smooth or velvety type, dry whitish, grayish, dirty gray, olive-gray skin. The flesh is white or yellowish in color, not very noticeably blue or red when cut. Old and overgrown fruiting bodies have a characteristic and clearly noticeable unpleasant odor. The leg area is ovoid or spherical, and may resemble a barrel or turnip in appearance, with a narrowing at the top.
It is impossible to cook such varieties together with edible fruiting bodies, since the entire finished dish will acquire a disgusting toxic taste and will be subject to mandatory disposal.
Where oak trees grow (video)
Taste and nutritional value of oak mushrooms
The nutritional value and taste characteristics of poultry mushrooms are due to the rich chemical composition mushroom pulp.
The nutritional value of 100 g of mushroom pulp is protein - 3.09 g, fat - 0.34 g, carbohydrates - 3.26 g with a total calorie content of 22-23 kcal.
Oak mushrooms in cooking
Before preparing mushrooms, it is necessary to carry out primary processing of the fruiting bodies, which, after being cleared of debris and soil, are washed and then boiled in salted water for a quarter of an hour. After the first boiling, the fruiting bodies are washed and boiled again.
Pickling
Pre-boiled mushrooms are laid out in sterile containers. glass jars, after which they are poured with boiling marinade prepared from a glass of water, five black peppercorns, a tablespoon of salt and a tablespoon of granulated sugar, five cloves of garlic, bay leaf and cloves. Before rolling, table vinegar is added to the jars.

Pickled oak mushrooms
Mushroom soup
Place pre-boiled mushrooms in boiling water and add salt, parsley, fresh or dried dill and black peppercorns - to taste. Grate the carrots on a coarse grater, finely chop the onion, then fry on vegetable oil until golden brown.
Diced potatoes are added to the boiling mushroom broth, and about a quarter of an hour before readiness, vegetable frying is added. It is advisable to serve the finished soup with fresh herbs and low-fat sour cream.